Διαφορά μεταξύ των αναθεωρήσεων του «Δρομολόγηση»
Itmy (συζήτηση | συνεισφορές) μ |
Itmy (συζήτηση | συνεισφορές) |
||
| (9 ενδιάμεσες αναθεωρήσεις από τον ίδιο χρήστη δεν εμφανίζεται) | |||
| Γραμμή 55: | Γραμμή 55: | ||
|} | |} | ||
==Θεωρία στην πράξη - OSPF στο MikroTik== | ==Θεωρία στην πράξη - OSPF στο MikroTik== | ||
| + | ===Τοπολογία=== | ||
| + | {| border="0" style="background:transparent;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
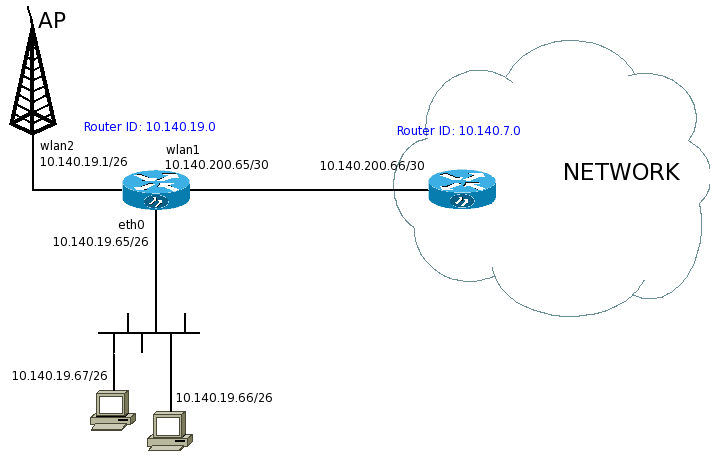
| + | |Έστω ότι θέλουμε να προσθέσουμε στο δίκτυο το ταρατσοPC/Routerboard μας που βρίσκεται στα αριστερά. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf topology.png|Τοπολογία του δικτύου για το παράδειγμα του OSPF]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Το μόνο που χρειάζεται να γνωρίζουμε είναι σε ποιον router θα συνδεθούμε (τo δίκτυο 10.140.200.64/30 στη συγκεκριμένη περίπτωση). | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | ===OSPF Settings=== | ||
| + | border="0" style="background:transparent;" | ||
| + | |||
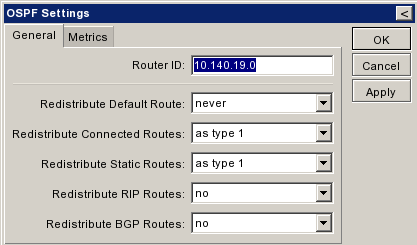
| + | Ξεκινάμε Routing>OSPF. Το πρώτο που πρέπει να κάνουμε είναι να ρυθμίσουμε τις βασικές παραμέτρους του OSPF στα Settings. Εκεί προσδιορίζουμε τα: | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf settings.png|frame|left|OSPF Settings]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Router Id''' | ||
| + | '''router-id''' (IP address; default: 0.0.0.0) - OSPF Router ID. If not specified, OSPF uses the largest IP address configured on the interfaces as its router ID | ||
| + | Συνήθως βάζουμε το subnet του κόμβου (π.χ. 10.140.19.0). | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Redistribute Default Route ''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | '''distribute-default''' (never | if-installed-as-type-1 | if-installed-as-type-2 | always-as-type-1 | always-as-type-2; default: never) - specifies how to distribute default route. Should be used for ABR (Area Border router) or ASBR (Autonomous System boundary router) settings | ||
| + | |||
| + | never - do not send own default route to other routers | ||
| + | |||
| + | if-installed-as-type-1 - send the default route with type 1 metric only if it has been installed (a static default route, or route added by DHCP, PPP, etc.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | if-installed-as-type-2 - send the default route with type 2 metric only if it has been installed (a static default route, or route added by DHCP, PPP, etc.) | ||
| + | |||
| + | always-as-type-1 - always send the default route with type 1 metric | ||
| + | |||
| + | always-as-type-2 - always send the default route with type 2 metric | ||
| + | |||
| + | NEVER Ώστε να μην κάνει announce to 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0 που προκαλεί χάος στο δίκτυο. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Connected Routes''' are created automatically when adding address to an interface. These routes specify networks, which can be accessed directly through the interface. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''redistribute-connected''' (as-type-1 | as-type-2 | no; default: no) - if set, the router will redistribute the information about all connected routes, i.e., routes to directly reachable networks. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Αν ενεργοποιήσουμε αυτή την επιλογή τότε όλα τα routes προς όλες τα subnets στα οποία ανήκουν οι ips των interfaces, γίνονται announce στους υπόλοιπους. Αυτό βολεύει στο να μην ξεχάσουμε να δηλώσουμε κάποιο subnet στο Networks. Μπορεί όμως να προκαλέσει προβήματα (όπως το να ανακοινώνει το private δικτυό μας στο υπόλοιπο δίκτυο). | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{Warning| Αν θέλουμε να βάλουμε σε ένα interface ip που ανηκει στο private δικτυο μας (π.χ. 192.168.Χ.Χ) | ||
| + | τότε πρέπει να απενεργοποιήσουμε την επιλογή '''Redistribute Connected Routes'''. | ||
| + | Διαφορετικά θα ανακοινώνουμε στους άλλους routers το subnet 192.168.x.x/y.}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''Static Routes''' are user-defined routes that specify a specific destination for packets moving through the router between a source and a destination. Static routes are important if it is not possible to build a route to a particular destination. They are useful for specifying the default gateway to which all unroutable packets will be sent. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''redistribute-static''' (as-type-1 | as-type-2 | no; default: no) - if set, the router will redistribute the information about all static routes added to its routing database, i.e., routes that have been created using the /ip route add command | ||
| + | |||
| + | Redistribute Static Routes -> As type 1 Ώστε να ανακοινώνει τα όποια static routes έχουμε (σε περίπτωση π.χ που έχουμε κόψει subnet για κάποιον που μπαίνει στην omni) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Χρήσιμο σε περίπτωση που θέλουμε να "κόψουμε" subnet στο AP για clients με πολλά pc και συνδέονται με router στο AP. Τότε το static route που προσδιορίζουμε στο IP>Routes γίνεται announce σε όλους τους routers. Διαφορετικά ο client με το subnet του δε θα βγαίνει στο υπόλοιπο δίκτυο. | ||
| + | |||
| + | *'''redistribute-rip''' (as-type-1 | as-type-2 | no; default: no) - with this setting enabled the router will redistribute the information about all routes learned by the RIP protocol. Εφόσον δε χρησιμοποιούμε RIP protocol το αφήνουμε no. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | *'''BGP Routes''' are dynamic routes, which have been created by the BGP protocol. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''redistribute-bgp''' (as-type-1 | as-type-2 | no; default: no) - with this setting enabled the router will redistribute the information about all routes learned by the BGP protocol. Εφόσον δε χρησιμοποιούμε BGP protocol το αφήνουμε no. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | References: http://www.mikrotik.com/documentation/manual_2.5/IP/Route.html | ||
| + | http://www.mikrotik.com/testdocs/ros/2.9/routing/ospf.php?notfound=6& | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Add Interfaces=== | ||
| + | {| border="0" style="background:transparent;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
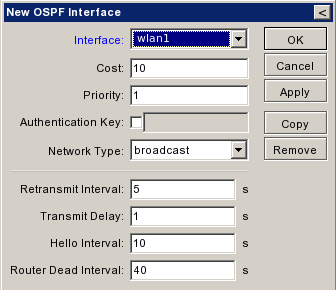
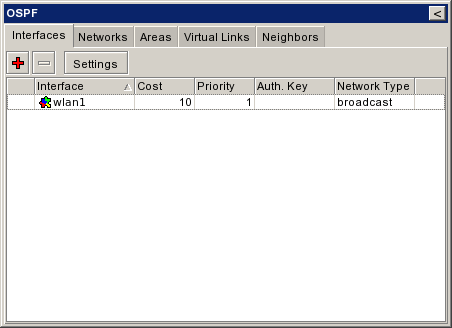
| + | |{{Warning|Εδώ προσθέτουμε τα backbone interfaces. Τίποτε Άλλο. Τα interfaces του ethernet ή του AP δεν πρεπει να προστίθενται.}} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf interfaces empty.png|frame|left|Add interfaces 1/3]] | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf interfaces new.png|frame|left|Add interfaces 2/3]] | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf interfaces wlan1.png|frame|left|Add interfaces 3/3]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
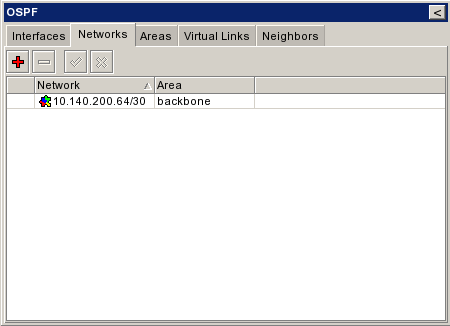
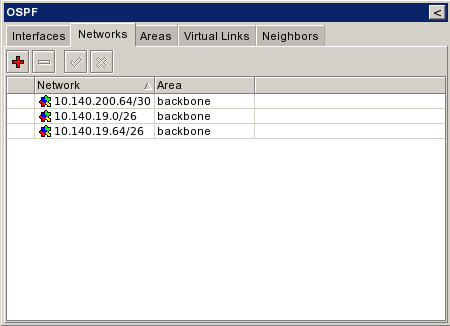
| + | ===Announce Networks=== | ||
| + | {| border="0" style="background:transparent;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
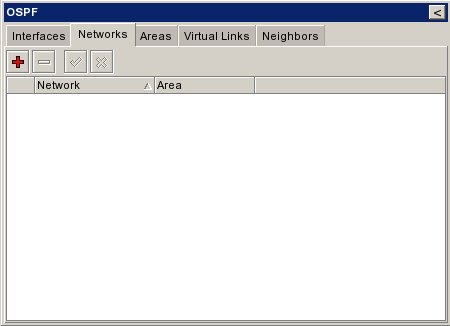
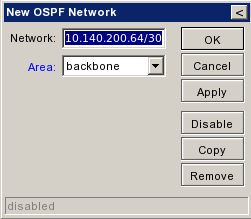
| + | ||{{Warning|Εδώ προσθέτουμε ΟΛΑ τα networks - εφόσον το redistribute connected routes ειναι no. }} | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf networks empty.png|frame|left|Add Networks 1/3]] | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf networks new.png|frame|left|Add Networks 2/3]] | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf networks.png|frame|left|Add Networks 3/3]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf_networks_full.png|frame|left|All Networks]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
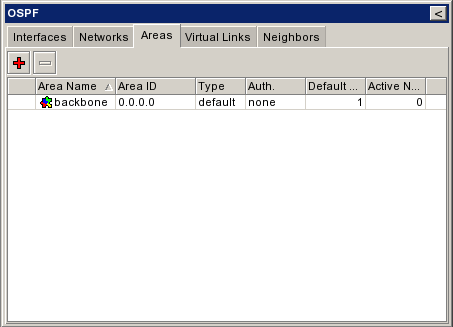
| + | ===Area=== | ||
| + | {| border="0" style="background:transparent;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf areas.png|frame|left|Area]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | | ||
| + | |} | ||
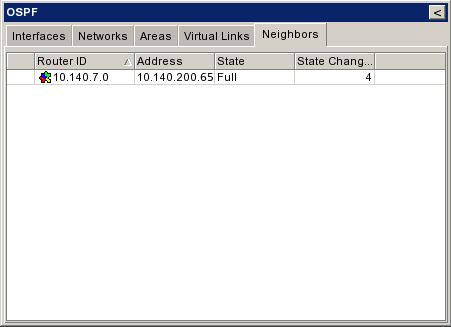
| + | ===Neighbors=== | ||
| + | {| border="0" style="background:transparent;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |Αν όλα πάνε καλά (δηλαδή και ο γειτονικός router έχει προσθέσει το interface και το network στον ospf του) τότε στο neighbors θα εμφανιζεται ενεργό το δίκτυο του backbone links μεταξύ σας. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ospf neighbors.png|frame|left|Neighbors]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | ===Routes=== | ||
| + | {| border="0" style="background:transparent;" | ||
| + | |- | ||
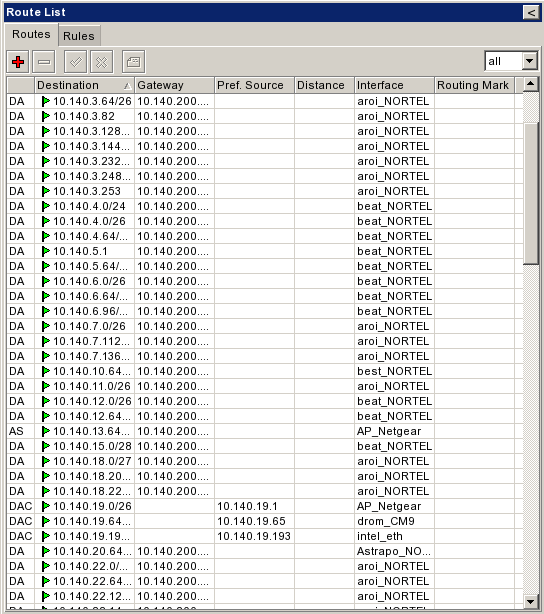
| + | |Ένας τελικός έλεγχος για να σιγουρευτούμε ότι όλα λειτουργούν σωστά είναι να κοιτάξουμε στο IP>Routes. Αν υπάρχουν πολλά routes (αρκετές σελίδες) τότε όλα λειτουργούν σωστά. Αν όμως υπάρχουν τα routes μόνο του router σας, τότε κάτι δε λειτουργεί σωστά. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Εικόνα:Ip routes.png|frame|left|IP>Routes]] | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Reference: http://www.mikrotik.com/testdocs/ros/2.9/refman2.9.pdf | ||
Τελευταία αναθεώρηση της 03:08, 1 Μαρτίου 2008
Λίγη Βασική Θεωρία[επεξεργασία]
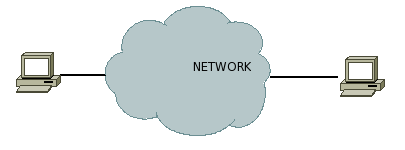
Δίκτυο Black Box[επεξεργασία]
|
Θέλετε μέσω ενός δικτύου (συννεφάκι) να επικοινωνήσετε από το pc σας (αριστερά) με ένα άλλο pc (δεξιά). Για να το κάνει αυτό ο υπολογιστής σας το μόνο που χρειάζεται να γνωρίζει είναι τη διεύθυνση του router στον οποιο συνδέεστε. Από εκεί και πέρα το τί συμβαίνει στο δίκτυο είναι άγνωστο για το pc. Παραδίδει δηλαδή τα δεδομένα στον router σε ένα πακέτο με προορισμό την ip του pc-δεξιά και τίποτε παραπάνω. Δε γνωρίζει ούτε πόσοι routers υπάρχουν ενδιάμεσα ούτε τι είδους links υπάρχουν μεταξύ τους. |
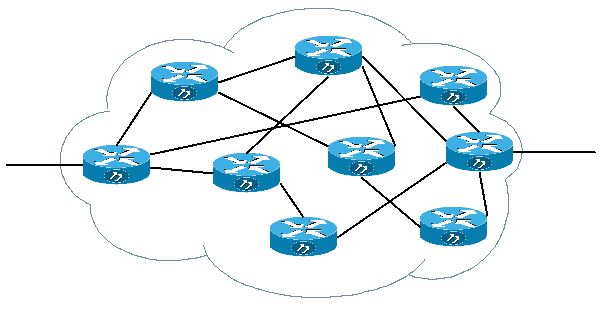
Το Εσωτερικό του Δικτύου[επεξεργασία]
| Εσωτερικά το δίκτυο μπορεί να είναι κάπως έτσι: |
| Οι routers είναι με κάποιο πολύπλοκο τρόπο διασυνδεδεμένοι μεταξύ τους και με κάποιο τρόπο πρέπει να ξέρει καθένας τους πού θα προωθεί τα πακέτα του ώστε να φτάσουν στον προορισμό τους. |
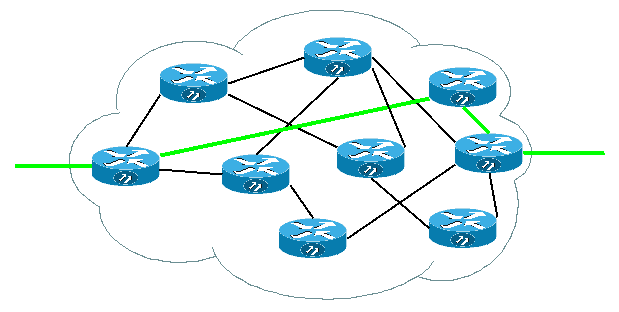
Διαδρομή μέσα στο Χάος[επεξεργασία]
Και για να βγάλουν άκρη ποιος συνδέεται με ποιον κλπ. χρειάζονται ένα ειδικό πρόγραμμα - το πρόγραμμα / αλγόριθμο δρομολόγησης (rip,ospf,bgp,olsr και πολλά άλλα).
Στόχος του αλγόριθμου δρομολόγησης είναι να βρεί μία πορεία μέσα στους routers που να συνδέει τον προορισμό με την αφετηρία. Για παράδειγμα ένας αλγόριθμος δρομολόγησης θα επιλέξει την πράσινη διαδρομή για να στείλει τα πακέτα από το ένα άκρο του δικτύου στο άλλο. |
Δυναμικός Αλγόριθμος Δρομολόγησης[επεξεργασία]
| Ένας δυναμικός αλγοριθμος δρομολόγησης (σαν αυτούς που υπάρχουν στα ospf,bgp,olsr) μπορεί να γνωρίζει πότε τα διάφορα links είναι up/down και ανάλογα αλλάζει τη διαδρομή δρομολόγησης ώστε πάντα τα πακέτα να φτάνουν στον προορισμό τους. Για παράδειγμα άν ένας router κλείσει (καθημερινό φαινόμενο για το wireless δίκτυο), το δυναμικό πρωτόκολλο δρομολόγησης (συγκεκριμένα το ospf στην περίπτωσή μας) θα επιλέξει άλλη εναλλακτική διαδρομή. |
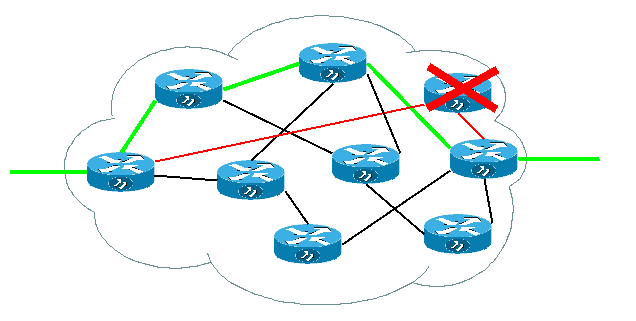
Distance Vector Αλγόριθμος Δρομολόγησης[επεξεργασία]
|
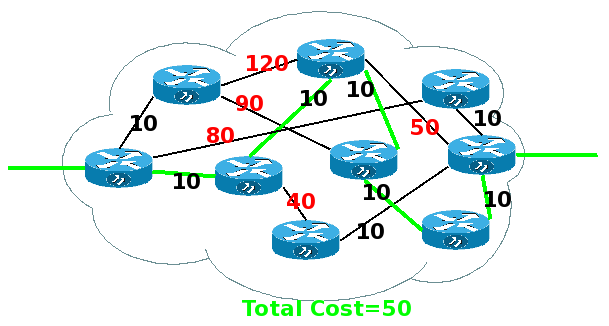
Μία επιπλέον πληροφορία που πρέπει να εκμεταλλευτούμε για την αποδοτική δρομολόγηση είναι η ποιότητα του κάθε link μεταξύ των routers. Σαν ποιότητα συμπεριλαμβάνουμε ταχύτητα, σταθερότητα, φόρτο κλπ. Αυτό το ποιοτικό χαρακτηριστικό της γραμμής το ποσοτικοποιούμε με το Cost της γραμμής. Όσο μεγαλύτερο Cost τόσο χειρότερο το link - ο αλγόριθμος δρομολόγησης προσπαθεί να το αποφύγει. Οι αλγόριθμοι που προσδιορίζουν τη διαδρομή με το ελάχιστο κόστος είναι οι distance vector αλγόριθμοι. Τέτοιον έχει και το ospf. Αυτοί οι αλγόριθμοι όπως είναι λογικό δεν επιλέγουν πάντοτε τη διαδρομή που περνά από το λιγότερο αριθμό routers (εφόσον υπάρχει άλλη με μικρότερο κόστος). Ένα παράδειγμα στο οποίο φαίνεται το παραπάνω είναι αυτό: |
Θεωρία στην πράξη - OSPF στο MikroTik[επεξεργασία]
Τοπολογία[επεξεργασία]
OSPF Settings[επεξεργασία]
border="0" style="background:transparent;"
Ξεκινάμε Routing>OSPF. Το πρώτο που πρέπει να κάνουμε είναι να ρυθμίσουμε τις βασικές παραμέτρους του OSPF στα Settings. Εκεί προσδιορίζουμε τα:
- Router Id
router-id (IP address; default: 0.0.0.0) - OSPF Router ID. If not specified, OSPF uses the largest IP address configured on the interfaces as its router ID Συνήθως βάζουμε το subnet του κόμβου (π.χ. 10.140.19.0).
- Redistribute Default Route
distribute-default (never | if-installed-as-type-1 | if-installed-as-type-2 | always-as-type-1 | always-as-type-2; default: never) - specifies how to distribute default route. Should be used for ABR (Area Border router) or ASBR (Autonomous System boundary router) settings
never - do not send own default route to other routers
if-installed-as-type-1 - send the default route with type 1 metric only if it has been installed (a static default route, or route added by DHCP, PPP, etc.)
if-installed-as-type-2 - send the default route with type 2 metric only if it has been installed (a static default route, or route added by DHCP, PPP, etc.)
always-as-type-1 - always send the default route with type 1 metric
always-as-type-2 - always send the default route with type 2 metric
NEVER Ώστε να μην κάνει announce to 0.0.0.0/0.0.0.0 που προκαλεί χάος στο δίκτυο.
- Connected Routes are created automatically when adding address to an interface. These routes specify networks, which can be accessed directly through the interface.
redistribute-connected (as-type-1 | as-type-2 | no; default: no) - if set, the router will redistribute the information about all connected routes, i.e., routes to directly reachable networks.
Αν ενεργοποιήσουμε αυτή την επιλογή τότε όλα τα routes προς όλες τα subnets στα οποία ανήκουν οι ips των interfaces, γίνονται announce στους υπόλοιπους. Αυτό βολεύει στο να μην ξεχάσουμε να δηλώσουμε κάποιο subnet στο Networks. Μπορεί όμως να προκαλέσει προβήματα (όπως το να ανακοινώνει το private δικτυό μας στο υπόλοιπο δίκτυο).
- Static Routes are user-defined routes that specify a specific destination for packets moving through the router between a source and a destination. Static routes are important if it is not possible to build a route to a particular destination. They are useful for specifying the default gateway to which all unroutable packets will be sent.
redistribute-static (as-type-1 | as-type-2 | no; default: no) - if set, the router will redistribute the information about all static routes added to its routing database, i.e., routes that have been created using the /ip route add command
Redistribute Static Routes -> As type 1 Ώστε να ανακοινώνει τα όποια static routes έχουμε (σε περίπτωση π.χ που έχουμε κόψει subnet για κάποιον που μπαίνει στην omni)
Χρήσιμο σε περίπτωση που θέλουμε να "κόψουμε" subnet στο AP για clients με πολλά pc και συνδέονται με router στο AP. Τότε το static route που προσδιορίζουμε στο IP>Routes γίνεται announce σε όλους τους routers. Διαφορετικά ο client με το subnet του δε θα βγαίνει στο υπόλοιπο δίκτυο.
- redistribute-rip (as-type-1 | as-type-2 | no; default: no) - with this setting enabled the router will redistribute the information about all routes learned by the RIP protocol. Εφόσον δε χρησιμοποιούμε RIP protocol το αφήνουμε no.
- BGP Routes are dynamic routes, which have been created by the BGP protocol.
redistribute-bgp (as-type-1 | as-type-2 | no; default: no) - with this setting enabled the router will redistribute the information about all routes learned by the BGP protocol. Εφόσον δε χρησιμοποιούμε BGP protocol το αφήνουμε no.
References: http://www.mikrotik.com/documentation/manual_2.5/IP/Route.html http://www.mikrotik.com/testdocs/ros/2.9/routing/ospf.php?notfound=6&
Add Interfaces[επεξεργασία]
Announce Networks[επεξεργασία]
Area[επεξεργασία]
Neighbors[επεξεργασία]
| Αν όλα πάνε καλά (δηλαδή και ο γειτονικός router έχει προσθέσει το interface και το network στον ospf του) τότε στο neighbors θα εμφανιζεται ενεργό το δίκτυο του backbone links μεταξύ σας. |
Routes[επεξεργασία]
| Ένας τελικός έλεγχος για να σιγουρευτούμε ότι όλα λειτουργούν σωστά είναι να κοιτάξουμε στο IP>Routes. Αν υπάρχουν πολλά routes (αρκετές σελίδες) τότε όλα λειτουργούν σωστά. Αν όμως υπάρχουν τα routes μόνο του router σας, τότε κάτι δε λειτουργεί σωστά. |
Reference: http://www.mikrotik.com/testdocs/ros/2.9/refman2.9.pdf